The aluminum extrusion process is a manufacturing method that involves shaping aluminum billets or logs into specific profiles or shapes. Aluminum extrusions have been around for over a century. The process was first developed in the early 1900s by Alfred Wilm, a German metallurgist. Wilm discovered that hot extrusion of aluminum could produce complex shapes with high strength and lightweight, making it ideal for industrial and architectural applications. Read More…
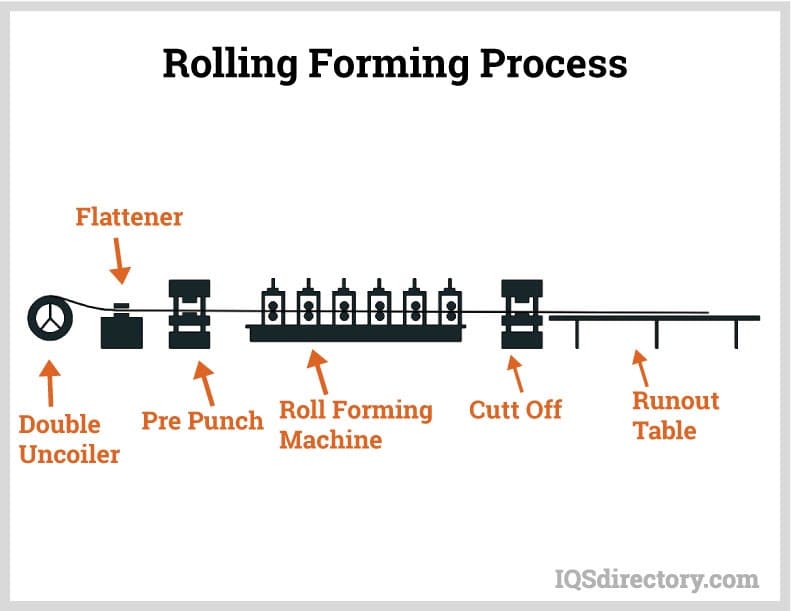
Since 1948, Johnson Brothers has been a leader in the aluminum roll forming industry. Our tooling can form different shapes with multiple bends & double thicknesses making a stronger part. Choose your type of outside edge, including hemmed designs. Our manufacturing procedure can take your part from concept to achievement. Please contact us today with any questions.

Quality Stamping & Tube Corp has been a leader in the aluminum extrusions and metal stamping industries for over 40 years. We attribute our success to our in-house die-making capabilities and wide range of extruded parts. All of our products are manufactured with quick turnaround and made to be high quality and durable. Our aluminum extrusions follow guidelines of up to 6 inches in diameter and...

Since 1986, GSH Industries has offered on time delivery and competitive pricing. With over 40,000 square feet of manufacturing, we offer aluminum extrusion products and services.
Dajcor Aluminum is the leading North American supplier of extruded, fabricated/machined, anodized and assembled components to the automotive, renewable energy, transportation, rail, marine, building trades, military, medical architectural and wall partition systems, office furniture, emergency vehicle and consumer product industries. Dajcor is an aluminum extrusion company with complete value add ...
More Aluminum Extrusions Manufacturers
A Brief History of Aluminum Extrusions
Aluminum extrusions trace their origins to the early 19th century, born from industrial innovation and the rise of aluminum as a versatile metal. The extrusion process began with British engineer Joseph Bramah, who patented a hydraulic extrusion press in 1797 for lead pipes. However, it wasn’t until aluminum’s commercial isolation in the 1850s—thanks to chemist Charles Martin Hall and the Hall-Héroult process—that extrusion found its star material.
By the 1880s, extrusion technology adapted to aluminum’s lightweight, malleable nature. Alexander Dick’s 1894 hot extrusion patent refined the method, using heat and pressure to force aluminum through dies, shaping beams, tubes, and custom profiles. Early adopters in Europe and the U.S. used these extrusions for structural frames and decorative trim, capitalizing on aluminum’s corrosion resistance and versatility.
The 20th century turbocharged demand for aluminum extrusions. World War I saw extrusions in aircraft frames—think early biplanes—while the 1930s brought Art Deco architecture with sleek aluminum window frames. Following World War II, the automotive and construction booms cemented their role; extrusions became key in car bumpers, highway signs, and skyscraper skeletons. During the aerospace race of the 1960s, aluminum extrusions were essential for lightweight, strong components in jets, rockets, and spacecraft.
Today, aluminum extrusions shape everything from solar panel frames and electric vehicle (EV) battery housings to advanced heat sinks and modular framing systems. The evolution of precision dies and the introduction of alloys such as 6061 and 6063 have enabled greater design freedom and higher performance. Modern extrusion lines now integrate computer numerical control (CNC) systems, robotics, and advanced quality control, making aluminum extrusions a cornerstone of modern design, manufacturing, and engineering.

The Aluminum Extrusion Process
The aluminum extrusion process begins with the selection of high-quality aluminum billets, which are then heated to a precise temperature and forced through a die under high pressure. This fundamental procedure is bifurcated into two primary methods: hot extrusion and cold extrusion, each suited for distinct applications and offering unique advantages. Understanding these extrusion techniques is essential for manufacturers, engineers, and buyers looking to optimize performance, cost, and quality.
- Hot Extrusion: This process involves heating the aluminum billet to approximately 450°C (850°F) or higher. The elevated temperature significantly enhances the aluminum’s plasticity, facilitating the production of large, intricate profiles with precise geometric tolerances. The billet, once heated, is subjected to high-pressure extrusion through a die, enabling the formation of complex shapes such as channels, T-slots, tubes, and multi-void profiles. Hot extrusion is particularly advantageous for manufacturing components that demand intricate designs and robust mechanical properties, such as those used in the aerospace, automotive, and construction sectors. The high-temperature environment ensures the extrusions exhibit excellent mechanical strength, resistance to cracking, and are well-suited for load-bearing applications.
- Cold Extrusion: Performed at ambient temperature without preheating the billet, cold extrusion offers distinct benefits including superior surface finish and dimensional accuracy. This method is optimal for producing smaller, less complex profiles with uniform cross-sections. Cold extrusion is particularly effective for applications where tight tolerances, minimal surface defects, and high surface quality are critical, such as in the fabrication of electrical components, heat sinks, precision parts, and connectors. Additionally, cold extrusion is more energy-efficient compared to hot extrusion due to the absence of a heating phase, making it a cost-effective and sustainable option for many manufacturers.
The selection between hot and cold extrusion processes is dictated by various factors including profile size and complexity, required mechanical properties, dimensional precision, production volume, and surface finish requirements. Each method is strategically employed based on the specific needs of the application, ensuring the production of high-quality aluminum extrusions tailored to meet rigorous industry standards.
Interested in how different extrusion methods impact part performance and cost? Explore our aluminum profile guides for more technical insights and application recommendations.
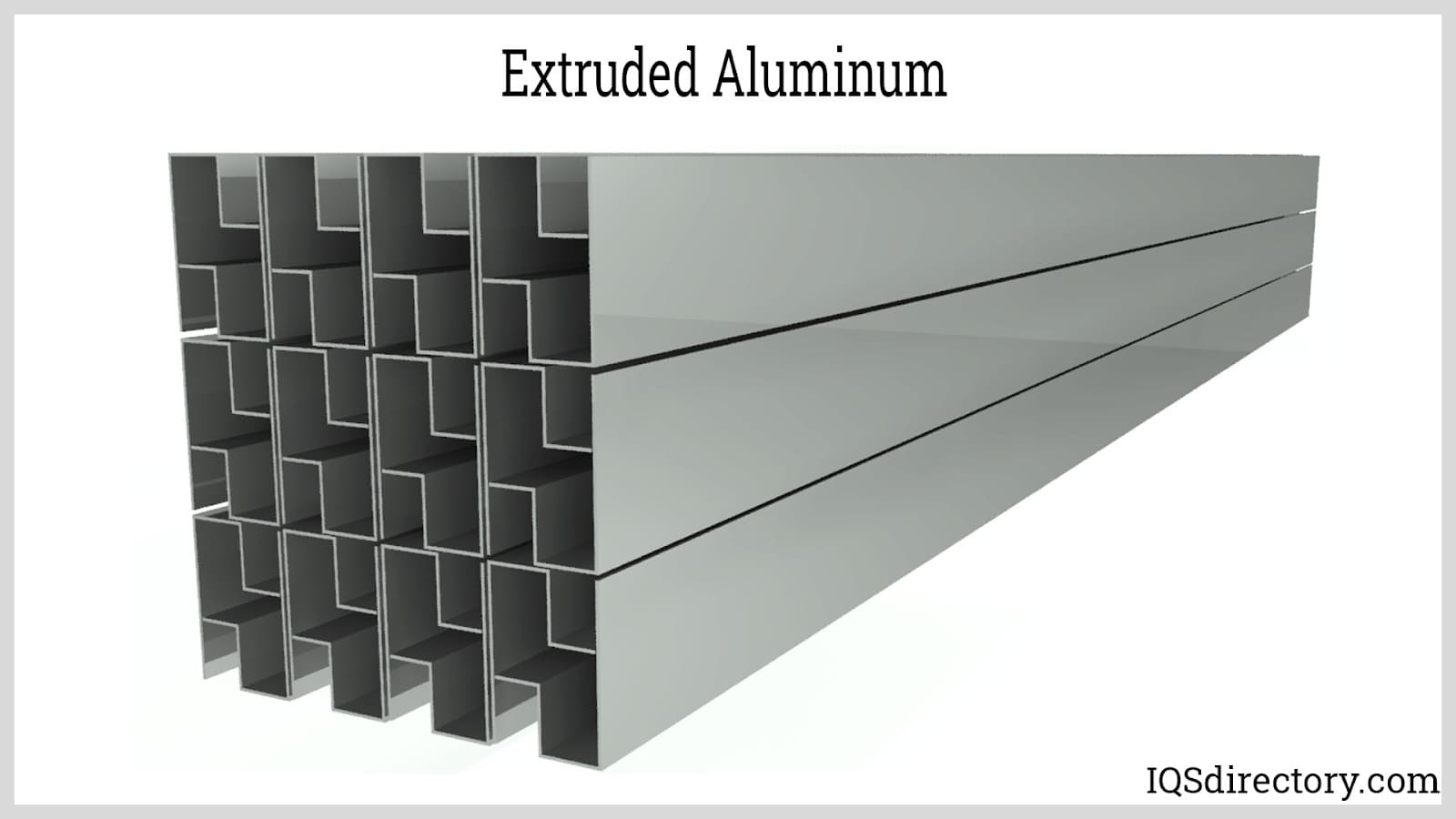
Various Types of Aluminum Extrusions
Aluminum extrusions are available in a diverse range of types, each suited for different functional, structural, and aesthetic demands. The flexibility of the extrusion process allows for a broad spectrum of extrusion profiles, catering to both standard and highly customized requirements.
- Standard Profiles: Featuring regular geometries such as squares, rectangles, rounds, angles, and channels, these profiles are extensively used across multiple industries due to their broad applicability and ready availability. Standard aluminum shapes are ideal for framing, supports, railings, tracks, and modular systems, making them a cost-effective option for high-volume and repeat applications.
- Custom Profiles: Precision-engineered to satisfy unique design specifications, custom aluminum extrusions allow for the creation of complex and intricate shapes that provide enhanced design flexibility. This customization capability is particularly valuable for applications requiring bespoke solutions—such as unique architectural features, proprietary hardware, or specialized equipment frames. Custom dies enable the integration of multiple functions into a single part, reducing assembly costs and improving product performance.
- Hollow vs. Solid Profiles: Aluminum extrusions are further classified into hollow and solid profiles. Hollow profiles, characterized by their open cross-sections (e.g., tubes, square tubing, channels), offer a lightweight yet structurally efficient option. They are integral to applications where weight reduction is paramount, such as in the aerospace, transportation, and automotive sectors. Conversely, solid profiles (e.g., bars, rods, flats), with their continuous, solid cross-sections, are favored in applications demanding superior strength, rigidity, and load-bearing capacity.
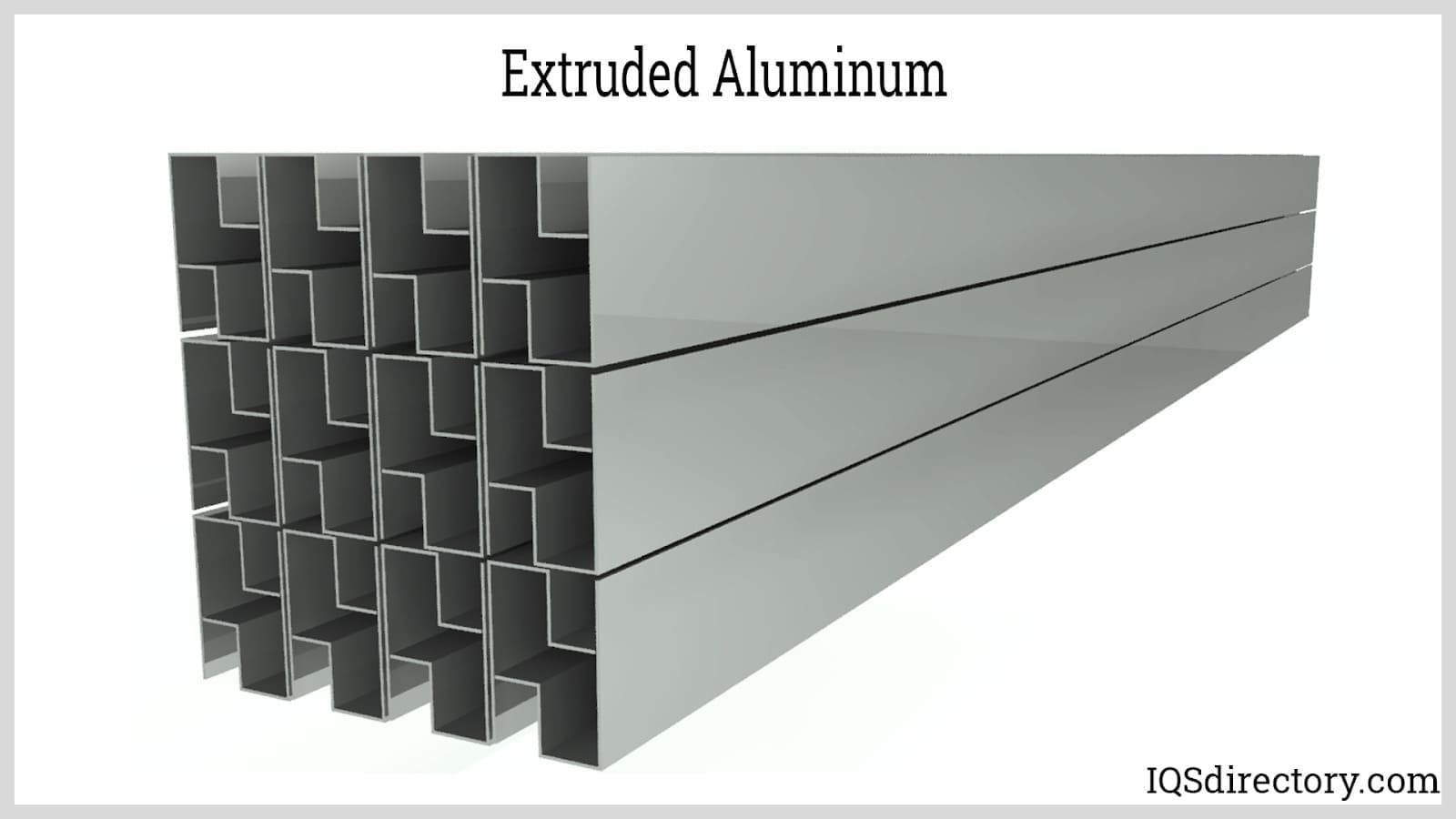
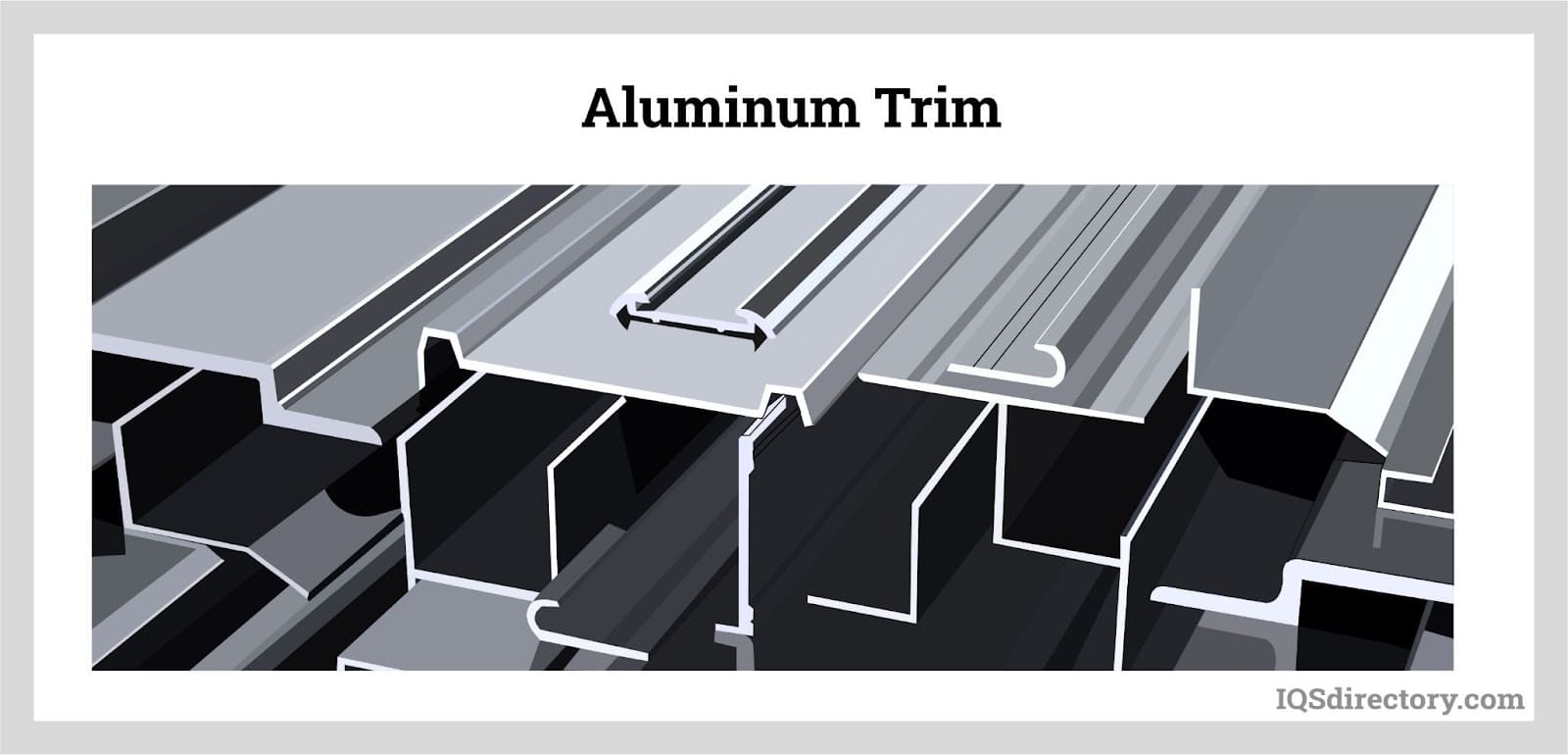
- Structural vs. Decorative Profiles: Structural profiles are designed to endure substantial loads and provide essential support in construction, engineering, and industrial projects, where strength, fatigue resistance, and durability are critical. Decorative profiles, meanwhile, focus on enhancing aesthetic appeal, making them suitable for architectural elements, consumer products, and furniture where visual impact and surface finish are priorities.
When selecting aluminum extrusions, manufacturers and designers must consider factors such as functionality, structural integrity, aesthetics, ease of assembly, and specific material properties. This versatility underpins the widespread adoption of aluminum extrusions across industries including construction, transportation, electronics, renewable energy, and consumer goods.
Looking for an extrusion profile that fits your project? Start by browsing our aluminum shapes or custom profile listings.
Aluminum Alloy Series Used for Extrusions
When it comes to aluminum, selecting the optimal alloy is critical for achieving the desired properties in extruded products. The most commonly recognized aluminum alloy series include the 1xxx, 2xxx, 3xxx, 4xxx, 5xxx, 6xxx, 7xxx, and 8xxx series. Each series is defined by its main alloying element, which imparts specific mechanical, thermal, and corrosion resistance characteristics.
- 1xxx Series: Comprising nearly pure aluminum (99%+), this series offers excellent corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity. It is primarily used where high conductivity is needed, such as in electrical busbars and heat exchangers.
- 2xxx Series: Featuring copper as the primary alloying element, these alloys provide high strength and hardness but lower corrosion resistance. They are typically used in aerospace and high-performance applications.
- 3xxx Series: Manganese-based alloys provide good formability and moderate strength, making them suitable for heat exchangers, beverage cans, and cooking utensils.
- 4xxx Series: With silicon as the main alloying element, these alloys are known for their good wear resistance and are commonly used in welding wire and automotive parts.
- 5xxx Series: Including alloys like 5052 and 5083, the 5xxx series is renowned for exceptional corrosion resistance and good weldability, thanks to magnesium as the primary alloying element. These non-heat-treatable alloys are ideal for marine, architectural, and chemical processing industries where exposure to harsh environments is common.
- 6xxx Series: The most popular choice for aluminum extrusions, particularly alloys such as 6061 and 6063, which balance strength, formability, and corrosion resistance. With magnesium and silicon as their main alloying elements, these alloys are easy to extrude, weld, and surface finish, making them ideal for construction, automotive, electronics, and consumer products.
- 7xxx Series: Containing zinc as the main alloying element, these high-strength alloys are used in aerospace, sporting equipment, and military hardware where maximum strength and toughness are required.
- 8xxx Series: These alloys feature other elements such as lithium and are used in specialized applications like aerospace and packaging.
The choice of alloy series directly impacts extrusion performance, product lifespan, and suitability for specific applications. For example, 6063 is often used for architectural trim, curtain walls, and window frames due to its superior surface finish, while 6061 is preferred for structural components in automotive and industrial machinery.
Our team of extrusion experts carefully selects the appropriate alloy series to ensure that your extruded aluminum products meet all performance and functionality expectations. Whether you require high tensile strength, excellent corrosion resistance, superior machinability, or thermal conductivity, we have the right alloy for your needs.
Need help choosing the best alloy for your project? Contact leading aluminum extrusion manufacturers for expert advice and quotes.

What are the Limitations of Aluminum Extrusions?
While aluminum extrusions offer remarkable versatility, there are inherent limitations to consider when specifying or sourcing extruded profiles. Recognizing these constraints is essential for optimal product design and application success.
- Size Constraints: Extrusion presses have a finite “circle size”—the maximum diameter of the die—typically maxing out at 12 to 14 inches for standard equipment, with larger presses (up to 20 inches) available at higher cost. This limits the maximum width or cross-sectional area of a single extrusion, making massive one-piece structures challenging or impractical.
- Strength Limitations: While alloys like 6061 provide decent tensile strength (approximately 45,000 PSI), aluminum extrusions cannot match the robustness of steel for heavy load-bearing applications. For example, bridge girders and large support beams may require steel or other high-strength materials instead of aluminum.
- Geometric Complexity: Extremely intricate profiles with thin walls, sharp angles, or deep recesses may be prone to distortion, cracking, or reduced structural integrity during extrusion. Compared to casting or machining, the geometric freedom of extrusion is somewhat limited.
- Tolerances: While extrusions can achieve tight tolerances (±0.01 inch), they may not be suitable for applications requiring ultra-high precision, such as certain aerospace or medical device components that may need post-extrusion machining.
- Thermal Conductivity: Although aluminum’s high thermal conductivity is a benefit in many applications (e.g., heat sinks), it can be a drawback in scenarios where thermal insulation is required.
- Customization Costs: Creating custom dies for unique profiles can be costly, with prices ranging from $500 to $5,000 or more. Low-volume production runs may not justify the upfront investment in tooling, making standard profiles more economical for smaller projects.
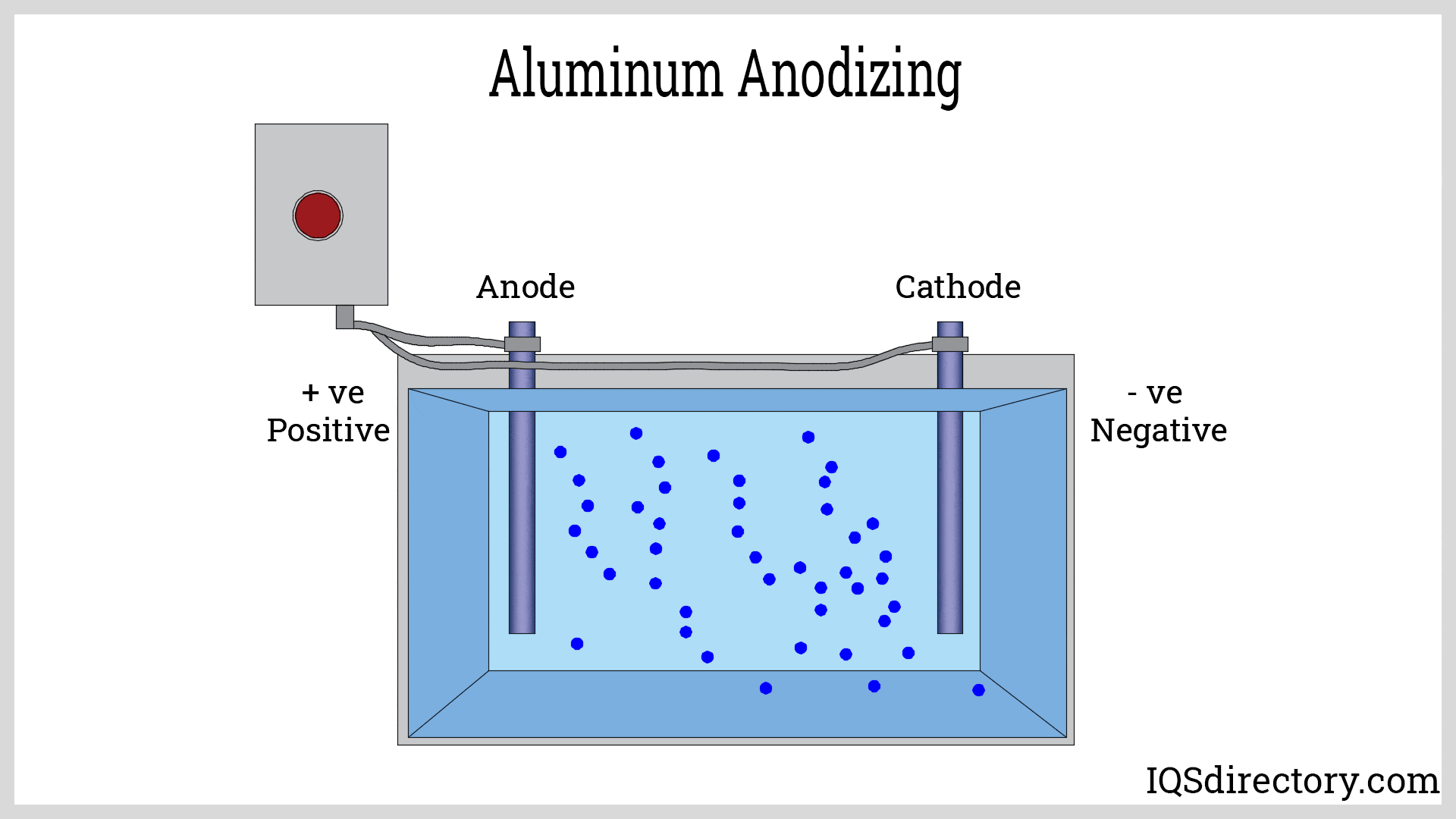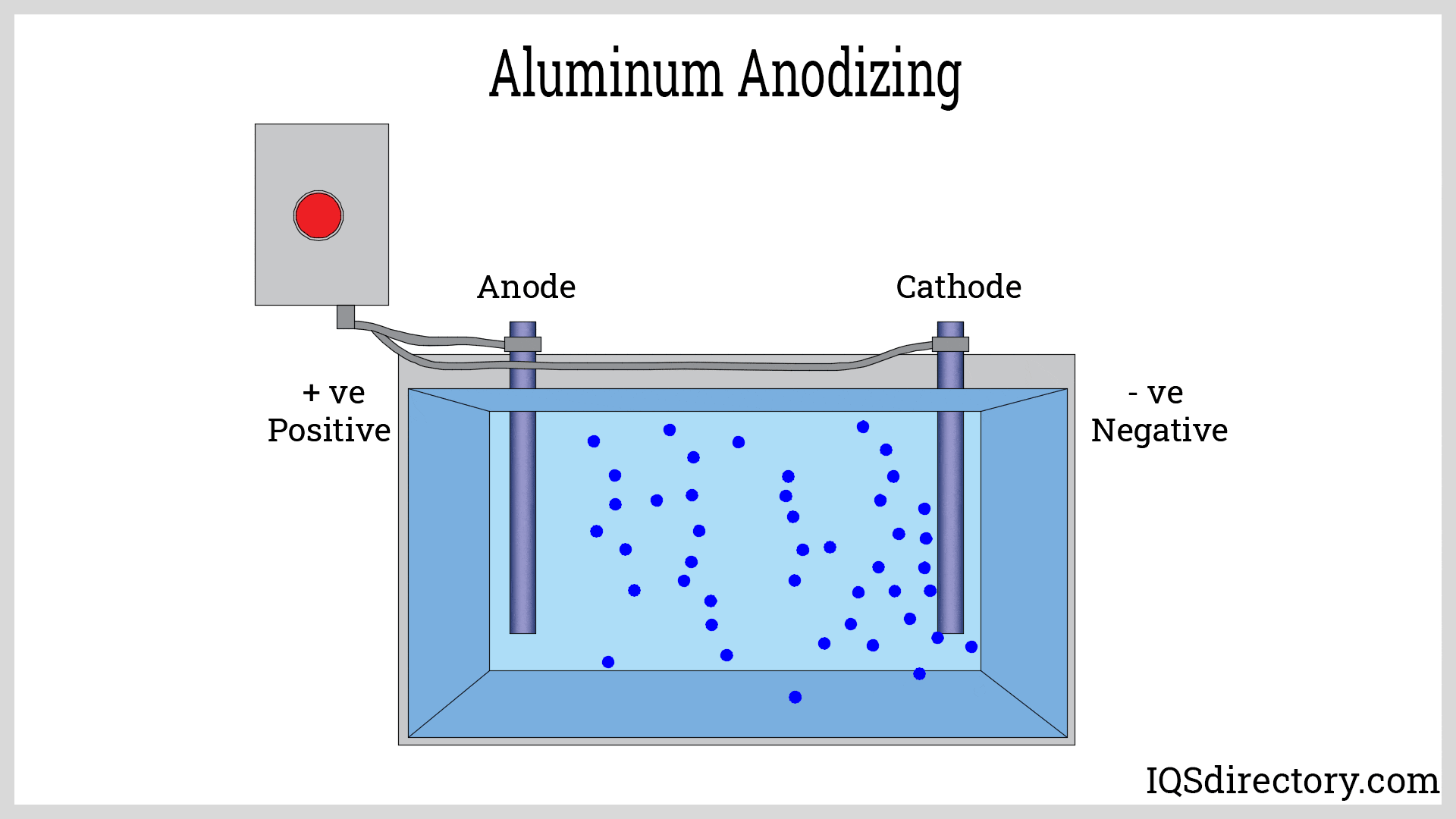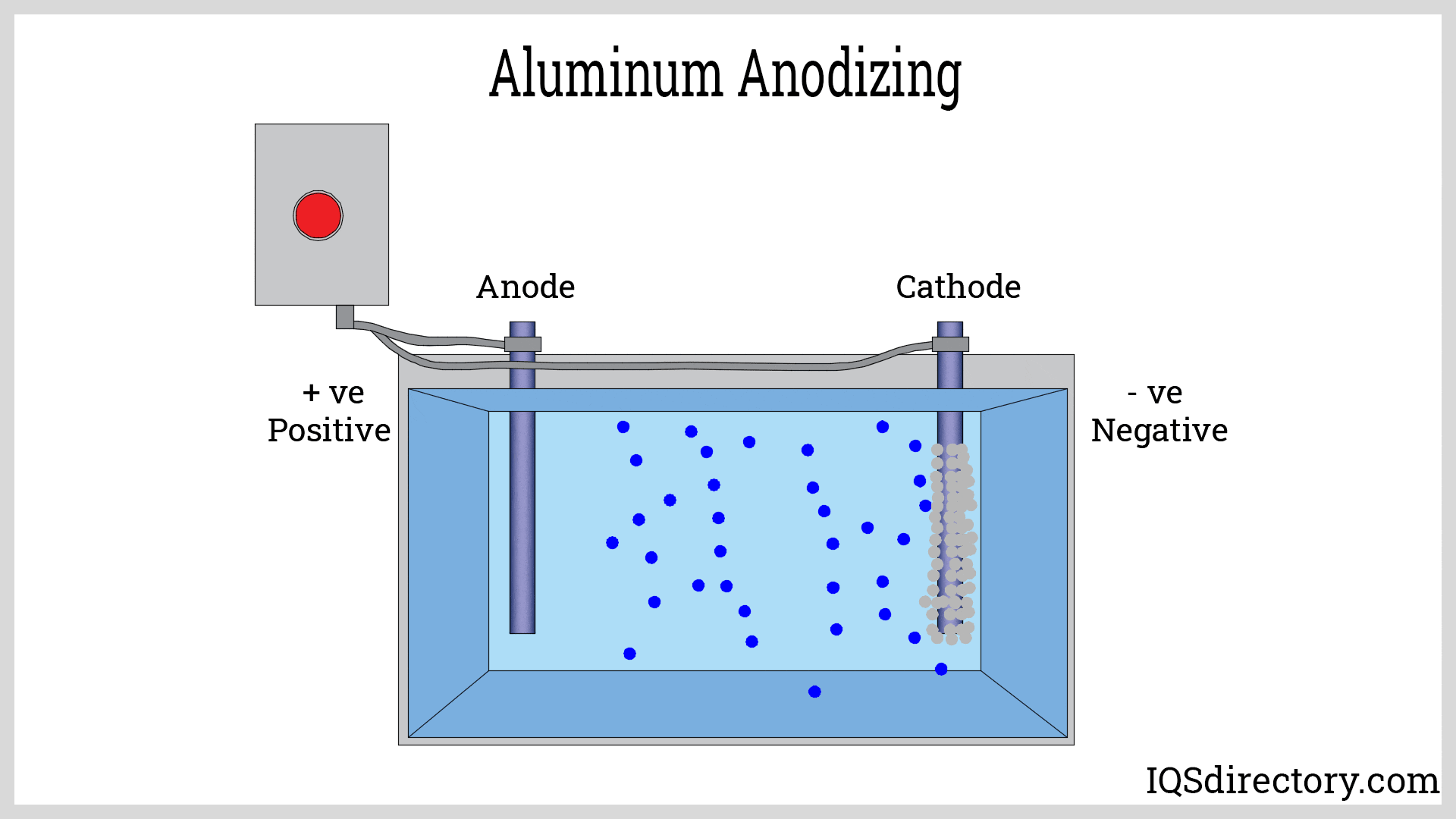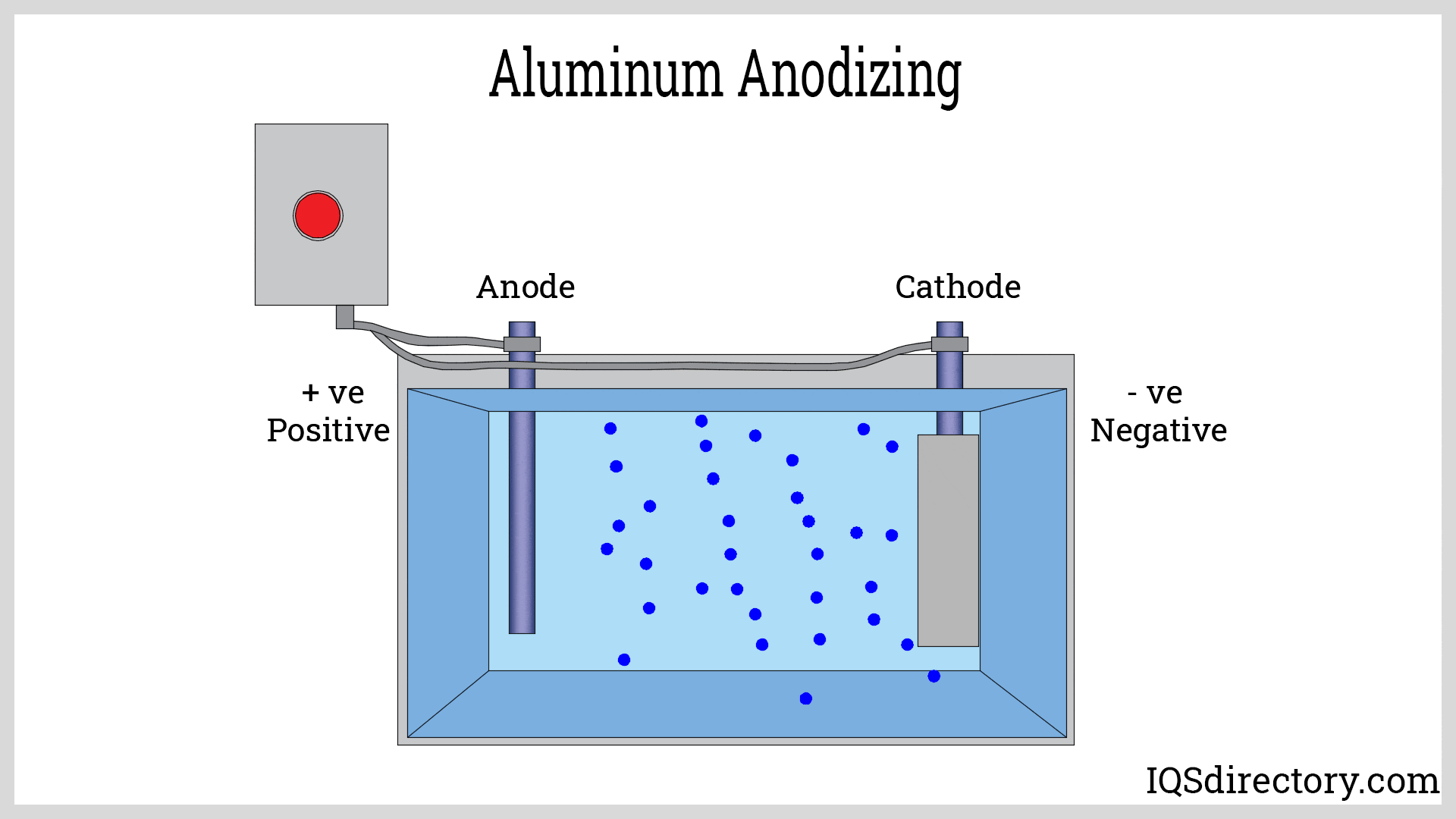
- Surface Finish Options: While anodizing and powder coating are available, more complex or decorative surface finishes may require additional post-processing, increasing lead times and costs.
Understanding these trade-offs allows buyers, engineers, and designers to leverage the strengths of aluminum extrusions while mitigating potential challenges through clever design, appropriate material selection, and post-processing steps.
Have specific requirements or concerns about your application? Request guidance from expert aluminum extrusion suppliers to optimize your project.
What are the Benefits of Aluminum Extrusions?
Aluminum extrusions offer a suite of advantages that make them a preferred material solution across various industries. Their unique combination of properties supports innovative designs, efficient manufacturing, and sustainable practices.
- High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Aluminum alloys such as 6063 or 6061 deliver impressive structural integrity at a fraction of steel’s weight. For example, a 10-foot extruded beam may weigh as little as 5 pounds, making aluminum ideal for lightweight frames in automotive, aerospace, and building construction.
- Corrosion Resistance: Aluminum naturally forms a protective oxide layer, enabling extrusions to resist rust and degradation even in harsh, wet, or salty environments. This property is essential for coastal railings, marine fittings, outdoor enclosures, and architectural elements exposed to the elements.
- Design Versatility: The extrusion process allows for the creation of complex profiles—channels, tubes, angles, T-slots, and multi-chamber shapes—tailored to exact requirements. This flexibility enables single extrusions to replace multiple parts, reducing assembly time and simplifying construction.
- Cost-Effectiveness: The relatively low cost of standard dies and the efficiency of high-volume production make aluminum extrusions a budget-friendly choice. Per-unit costs decrease significantly with scale, making them suitable for mass-produced components like solar panel mounts, window frames, and modular systems.
- Thermal and Electrical Conductivity: Aluminum extrusions are excellent for heat dissipation in electronics (heat sinks) and for conducting electricity in power transmission (busbars). Their superior conductivity improves system performance and reliability.
- Surface Finishing Options: Processes such as anodizing, powder coating, and painting enhance aesthetics, color selection, and wear resistance without significant weight gain. These finishes also improve corrosion protection and allow for branding or decorative effects.
- Sustainability: Aluminum is highly recyclable, with more than 75% of all aluminum ever produced still in use today. The extrusion process itself generates minimal waste, and recycling aluminum requires substantially less energy than primary production. This makes aluminum extrusions a top choice for eco-friendly, circular economy, and green building initiatives.
- Low Maintenance: The durability and corrosion resistance of aluminum extrusions translate to minimal maintenance requirements, reducing long-term operational costs for owners and facility managers.
Furthermore, aluminum’s ease of fabrication and compatibility with cutting, drilling, welding, and joining techniques make it easy to integrate extrusions into larger assemblies or custom products.
Aluminum extrusions are an ideal solution for a wide range of applications—from construction and automotive to renewable energy, electronics, marine, medical, and consumer goods—delivering lightweight strength, adaptability, and value that are hard to match with other materials.
Ready to unlock the benefits of aluminum extrusions for your next project? Browse our list of trusted extrusion suppliers or request a custom quote today.
Applications of Aluminum Extrusions
Aluminum extrusions are used in a wide variety of industries, thanks to their unique blend of strength, light weight, corrosion resistance, and design flexibility. Below are some of the most common and high-growth applications for extruded aluminum products:
Building and Construction
Aluminum extrusions are an excellent choice for the construction industry due to their lightweight nature, high strength, and exceptional corrosion resistance. You’ll find extruded aluminum in a variety of applications, such as window and door frames, curtain walls, skylights, roofing systems, structural supports, handrails, and modular office partitions. They’re ideal for creating durable and long-lasting building components that ensure both structural integrity and aesthetic appeal in modern architecture.

Automotive Industry
Aluminum extrusions have long been integral to the automotive industry, particularly for structural components like body frames, engine parts, crash management systems, bumper beams, roof rails, battery enclosures, and suspension systems. Their lightweight yet high-strength properties significantly contribute to enhancing fuel efficiency, reducing emissions, and improving safety. The ability to extrude complex, precision-engineered profiles enables the creation of components that meet stringent performance and safety standards while also addressing the industry’s increasing demand for lightweight materials and electric vehicle designs.
Aerospace Industry
Aluminum extrusions are extensively utilized in the aerospace industry, primarily due to their superior strength-to-weight ratio and excellent corrosion resistance. These properties make them ideal for critical applications such as aircraft frames, wings, fuselages, landing gear, seat tracks, and cargo holds. Extruded aluminum is also integral in manufacturing rocket components, satellite structures, and drone frames, as it maintains structural integrity under extreme conditions and minimizes overall system weight.
Electrical Industry
Aluminum extrusions are an excellent choice for the electrical industry, frequently used for applications such as electrical enclosures, busbars, heat sinks, power distribution systems, and lighting fixtures. Their high thermal conductivity ensures efficient heat dissipation for electronic components, while their excellent electrical conductivity makes them ideal for power transmission and distribution systems. Extruded aluminum can be custom-designed for optimal cooling, compactness, and electrical performance.
Medical Equipment
Aluminum extrusions are an ideal choice for manufacturing medical equipment, including wheelchair frames, hospital beds, diagnostic equipment housings, surgical instruments, laboratory furniture, and cleanroom systems. They provide a lightweight yet durable solution, ensuring ease of handling and longevity. Additionally, aluminum extrusions are easy to clean, sanitize, and maintain, meeting the strict hygiene standards required in medical environments. Their robustness and versatility make them perfect for creating reliable and high-quality medical devices that meet regulatory requirements.
Renewable Energy
Aluminum extrusions are gaining significant traction in the renewable energy sector, particularly for applications such as solar panel frames, mounting brackets, wind turbine components, inverter housings, and battery enclosures. Their lightweight yet high-strength properties make them ideal for structures that must endure harsh environmental conditions. Their corrosion resistance and durability ensure long-term performance and reliability in demanding outdoor environments, further enhancing their suitability for renewable energy projects.
Consumer Products
Aluminum extrusions are widely used in various consumer products, including furniture, sporting equipment (bicycle frames, golf clubs), household appliances, electronics enclosures, shelving systems, and display stands. They provide a sleek, modern design while being lightweight and durable, making them an ideal choice for enhancing both the functionality and aesthetic appeal of these products.
Marine Applications
In the marine industry, aluminum extrusions are highly valued due to their superior corrosion resistance, lightweight properties, and excellent strength-to-weight ratio. These attributes make them indispensable in boat construction, where they are extensively utilized for fabricating structural components such as hulls, decks, bulkheads, superstructures, ladders, and railings. Their application not only enhances the durability and performance of marine vessels but also contributes to overall efficiency and cost-effectiveness in manufacturing and maintenance.
Are you exploring new applications for aluminum extrusions? See how leading manufacturers serve your industry by browsing our directory or requesting sample profiles today.
Choosing the Right Aluminum Extrusion Manufacturer
To achieve optimal results when procuring aluminum extrusions, it is crucial to evaluate several manufacturers through our comprehensive directory. Each manufacturer’s profile page showcases their experience, production capabilities, certifications (such as ISO 9001, IATF 16949, or AS9100), material specialties, and value-added services like CNC machining, anodizing, powder coating, and assembly. You’ll also find a contact form for further inquiries or quote requests, making it easy to compare options.
Utilize our patented website previewer to efficiently discern each company’s specialties, core competencies, and previous project examples. Finally, leverage our streamlined RFQ form to simultaneously contact multiple manufacturers with a single request, ensuring you gather competitive quotes and information for your project.
When selecting an aluminum extrusion supplier, consider factors such as minimum order quantities, lead times, design support, secondary processing capabilities (cutting, drilling, welding), finishing options, logistics, and quality assurance programs. Ask about in-house engineering services for help with profile optimization and cost reduction. Don’t forget to inquire about inventory management, custom packaging, and on-time delivery guarantees.
Ready to find the perfect partner for your next project? Compare aluminum extrusion manufacturers now or submit your RFQ for fast, competitive responses.
Check out our Metal Stampings website
Check out our Investment Castings website
What is the aluminum extrusion process?
The aluminum extrusion process involves heating high-quality aluminum billets and forcing them through a shaped die under high pressure. There are two main methods: hot extrusion, which is done at elevated temperatures for producing large or complex profiles, and cold extrusion, performed at room temperature for creating smaller or simpler profiles with excellent surface finish and dimensional accuracy.
What are common types of aluminum extrusions?
Common types of aluminum extrusions include standard profiles (such as squares, rectangles, rounds, angles, and channels), custom profiles designed for specific applications, hollow profiles like tubes and channels for lightweight structures, solid profiles for strength, structural profiles for load-bearing applications, and decorative profiles for aesthetic purposes.
Which aluminum alloy series are used for extrusions?
The main aluminum alloy series used for extrusions are 1xxx, 2xxx, 3xxx, 4xxx, 5xxx, 6xxx, 7xxx, and 8xxx, each offering unique properties. The 6xxx series, especially 6061 and 6063 alloys, are particularly popular due to their excellent balance of strength, formability, weldability, and corrosion resistance. Other series are selected for specific needs like conductivity, marine use, or high strength.
What are the benefits of using aluminum extrusions?
Aluminum extrusions provide an outstanding strength-to-weight ratio, high corrosion resistance, design versatility, cost-efficiency, and excellent thermal and electrical conductivity. They are easy to fabricate, allow for multiple finishing options, offer sustainability through recyclability, and require low maintenance over their service life.
What are the limitations of aluminum extrusions?
Limitations include size constraints defined by the press and die, lower strength compared to steel, challenges in achieving extremely complex or thin-walled profiles, certain tolerance limitations, possible high customization costs for unique dies, and the need for additional post-processing for advanced surface finishes or ultra-precise components.
In which industries are aluminum extrusions commonly used?
Aluminum extrusions are widely used in building and construction, automotive, aerospace, electrical, renewable energy, marine, medical equipment, and consumer products sectors. Their versatility, durability, and lightweight nature make them suitable for structural frames, enclosures, machinery components, window and door frames, solar panel mounts, and much more.
How do I choose the right aluminum extrusion manufacturer?
To choose the right aluminum extrusion manufacturer, evaluate their production capabilities, certifications, experience, materials and finishing options, design and engineering support, lead times, minimum order quantities, and value-added services. Comparing quotes, requesting samples, and reviewing previous projects are also recommended steps in the supplier selection process.





 Alloy Suppliers
Alloy Suppliers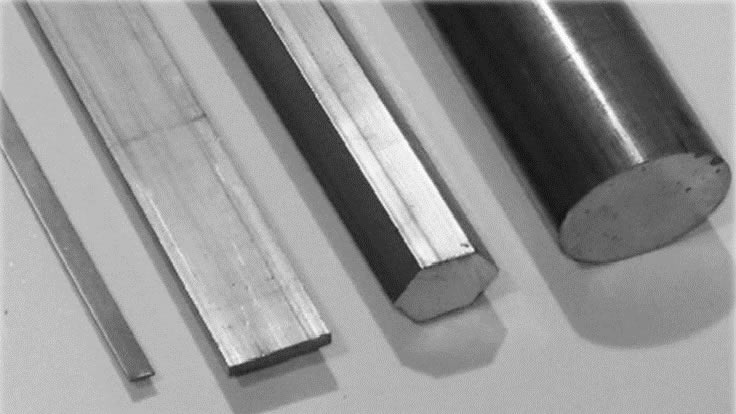 Aluminum
Aluminum Aluminum Extrusions
Aluminum Extrusions Copper-Brass-Bronze
Copper-Brass-Bronze Nickel
Nickel Magnets
Magnets Stainless Steel
Stainless Steel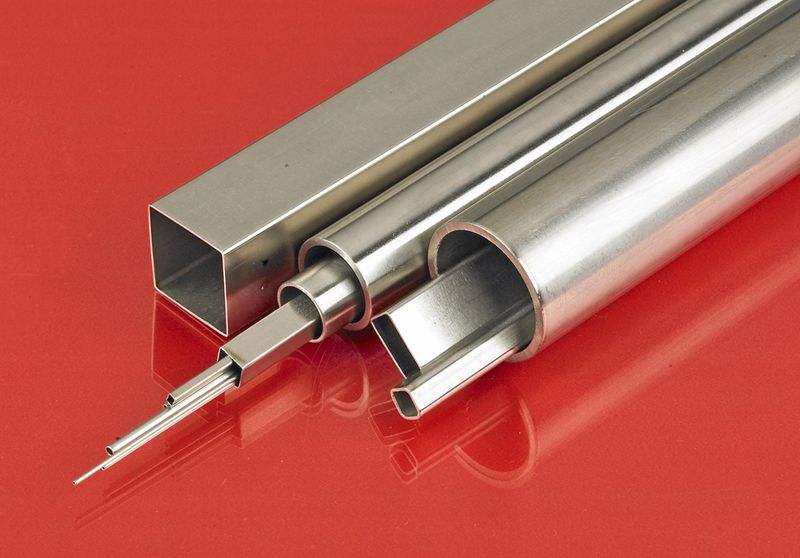 Stainless Steel Tubing
Stainless Steel Tubing Steel Service Centers
Steel Service Centers Titanium
Titanium Tungsten
Tungsten Wire Rope
Wire Rope Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services