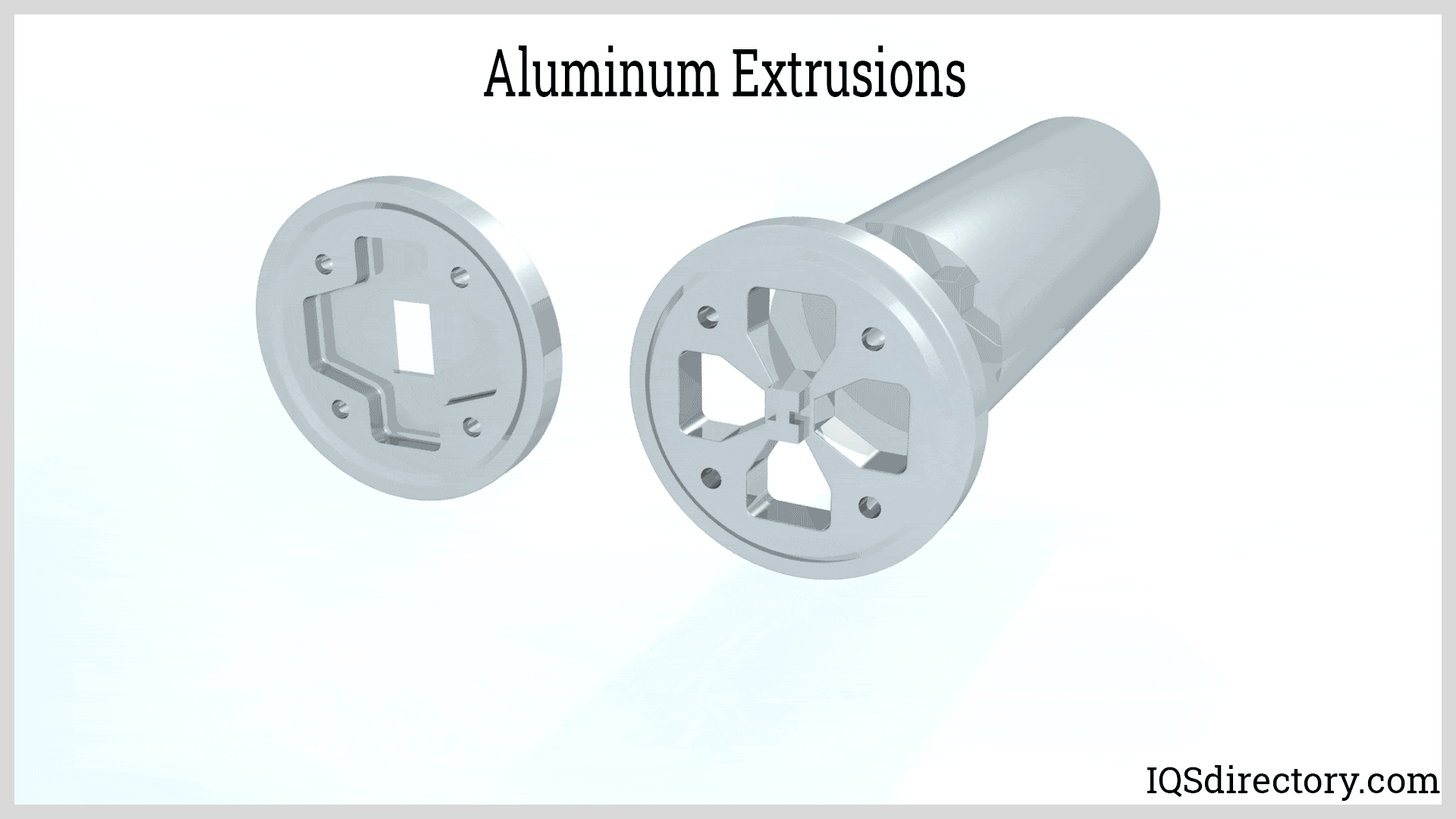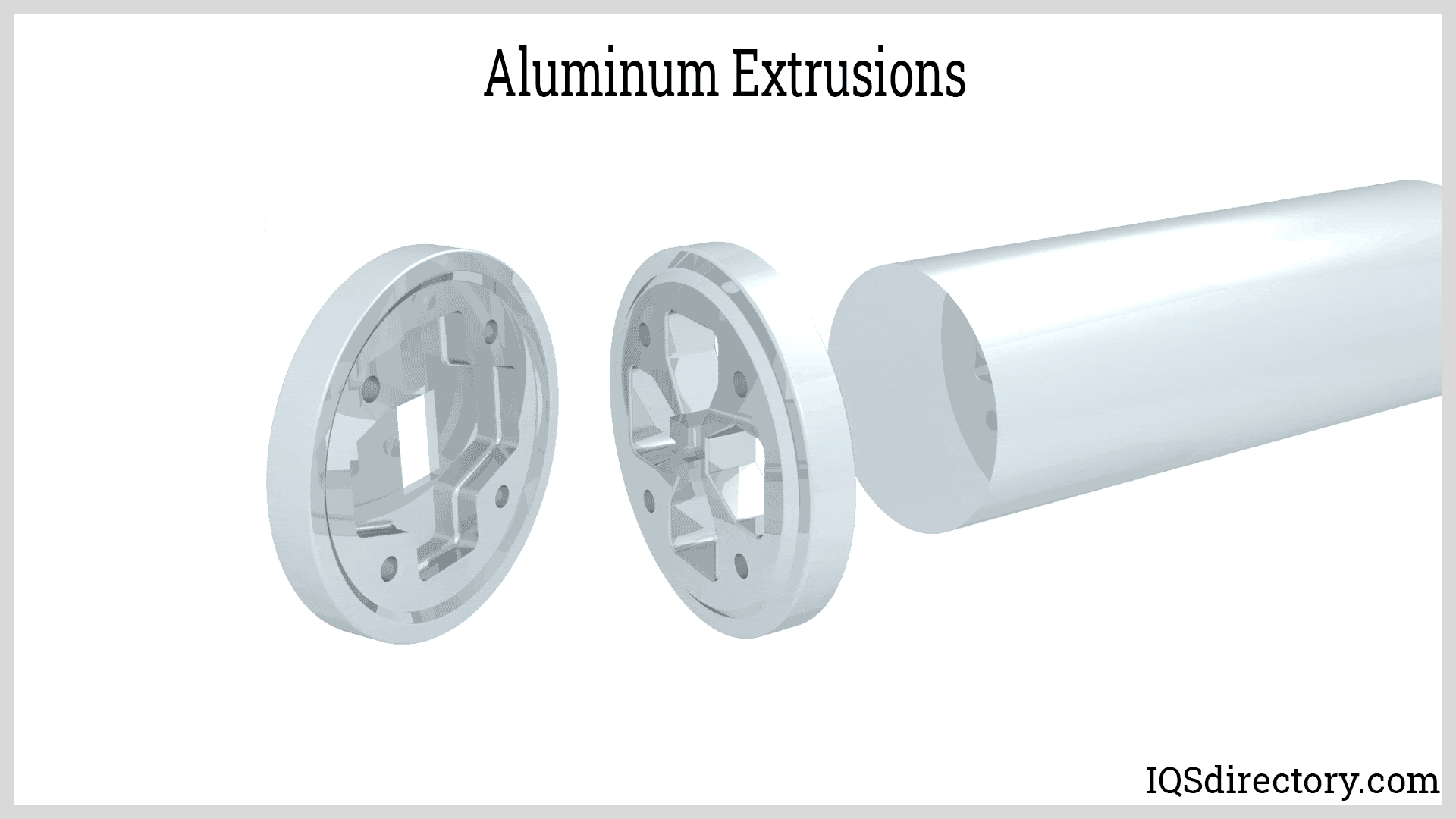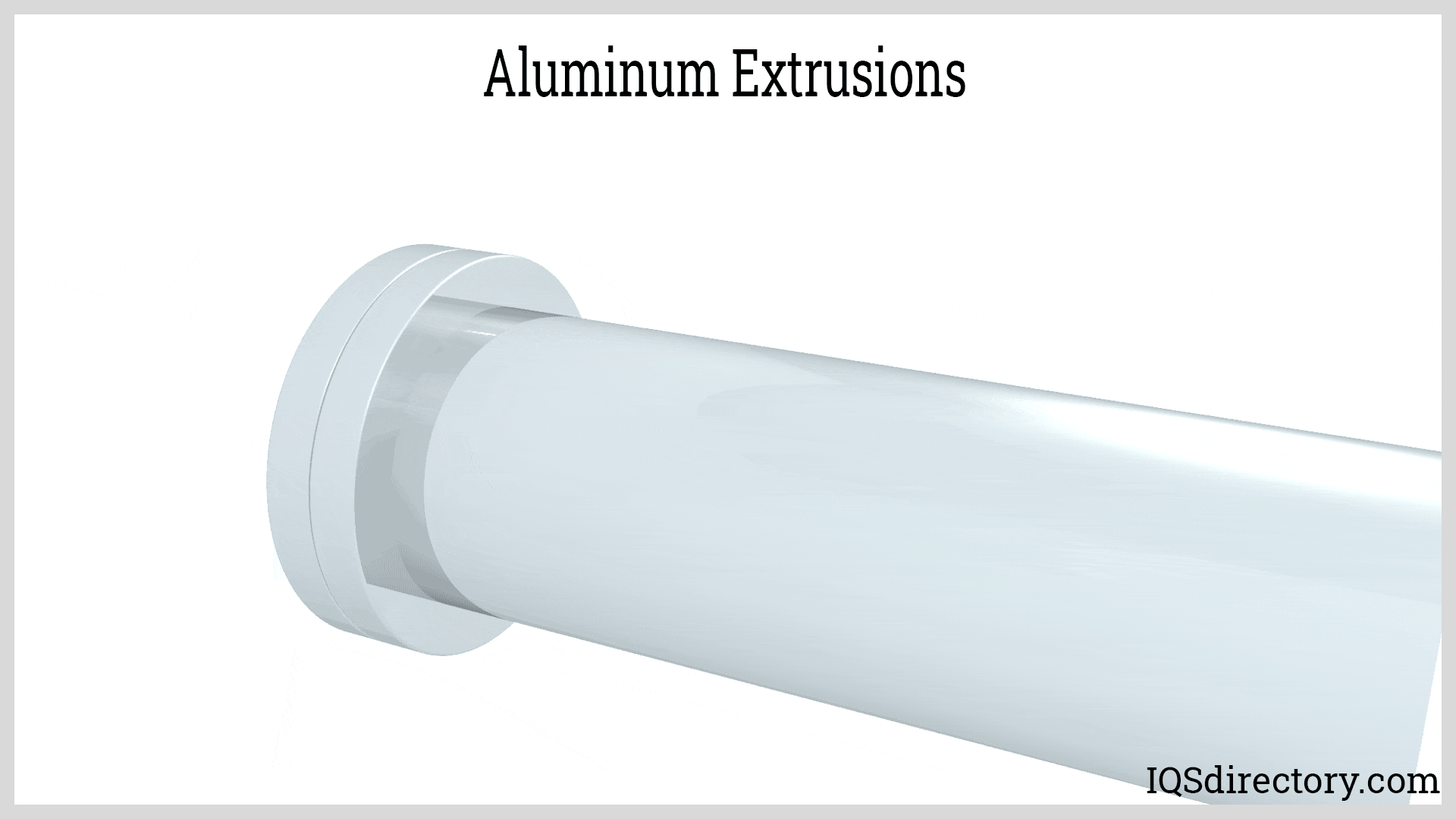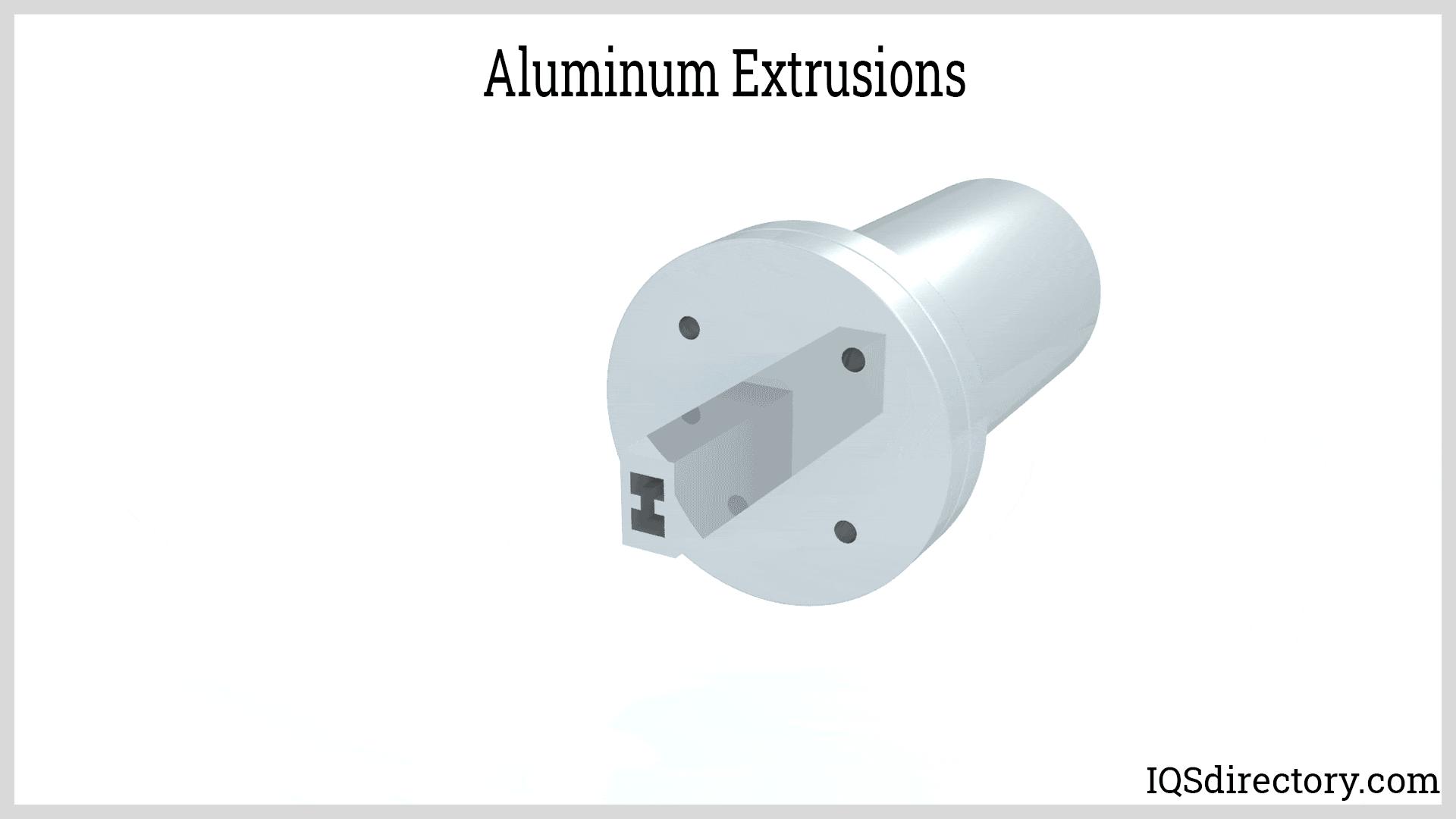
The profiles for aluminum extrusion are produced by dies configured and crafted to represent the desired design of the extruded product. They come in sizes and dimensions capable of meeting the requirements of any application. Read More…
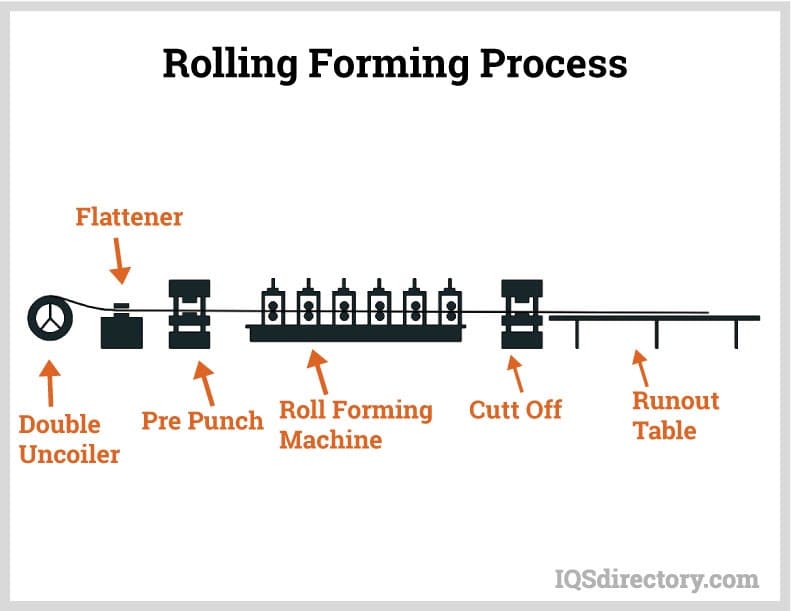
Since 1948, Johnson Brothers has been a leader in the aluminum roll forming industry. Our tooling can form different shapes with multiple bends & double thicknesses making a stronger part. Choose your type of outside edge, including hemmed designs. Our manufacturing procedure can take your part from concept to achievement. Please contact us today with any questions.

Quality Stamping & Tube Corp has been a leader in the aluminum extrusions and metal stamping industries for over 40 years. We attribute our success to our in-house die-making capabilities and wide range of extruded parts. All of our products are manufactured with quick turnaround and made to be high quality and durable. Our aluminum extrusions follow guidelines of up to 6 inches in diameter and...

Since 1986, GSH Industries has offered on time delivery and competitive pricing. With over 40,000 square feet of manufacturing, we offer aluminum extrusion products and services.
Dajcor Aluminum is the leading North American supplier of extruded, fabricated/machined, anodized and assembled components to the automotive, renewable energy, transportation, rail, marine, building trades, military, medical architectural and wall partition systems, office furniture, emergency vehicle and consumer product industries. Dajcor is an aluminum extrusion company with complete value add ...
More Aluminum Profile Manufacturers
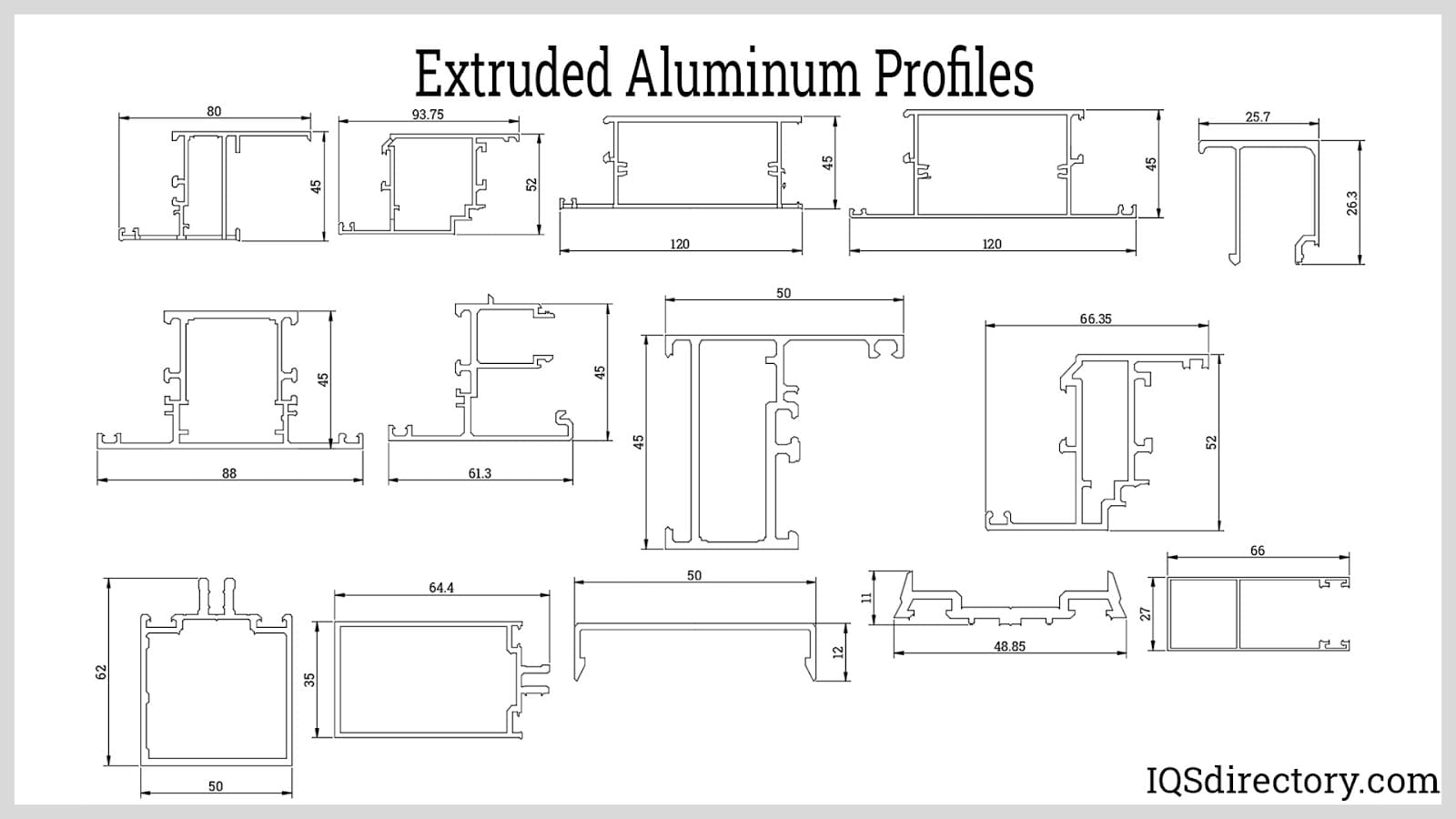
Aluminum profiles, also known as aluminum extrusions, are structural components manufactured from high-strength aluminum alloys. Despite the name, the extrusion dies used to create these profiles are made from hardened steel, allowing the same die to be used repeatedly without significant wear or loss of precision. This ensures aluminum profiles are produced with continuous, high-tolerance dimensions and consistent quality.
Common standard aluminum extrusion profiles include I beams, angle brackets, channels, tubes, and T-slot framing systems, all of which are widely used in industries such as construction, manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, and electronics.
In addition to these standard options, custom aluminum profiles are frequently engineered to suit unique design requirements for specialized applications. When custom extrusions are needed, customers can provide a CAD rendering or collaborate directly with experienced extrusion engineers and aluminum profile manufacturers to develop the desired cross-sectional shape, alloy type, surface finish, and mechanical specifications.
Aluminum Profile Manufacturing Process
The aluminum extrusion process is a precise and controlled method for creating long, uniform shapes from aluminum billets. This process is integral to the production of high-quality profiles for a wide variety of applications, from architectural frameworks to precision machinery components. Below, we outline the key stages in manufacturing aluminum profiles and explain how each step impacts the final product's quality and performance.
1. Preparing the Die
The process begins with the creation of a custom die, machined from a solid piece of hardened tool steel. The die is carefully designed to match the exact cross-sectional shape of the desired profile, ensuring dimensional accuracy and repeatability.
Prior to extrusion, the die is preheated to approximately 932 °F (500 °C) to facilitate even metal flow, reduce wear, and extend the die's operational life. This preheating step is crucial for minimizing internal stresses and producing consistent, high-quality extrusions.
2. Heating the Billet
The aluminum billet—a solid, cylindrical piece of aluminum alloy—is heated to a temperature where it becomes malleable but not molten (up to 932 °F / 500 °C for hot extrusion). Proper temperature control is essential to ensure smooth metal flow and prevent defects such as surface cracks or incomplete filling of the die cavity.
Cold extrusion is also possible, particularly for certain alloys and profile types, but hot extrusion is the most common method for architectural and industrial aluminum profiles.
3. Loading the Billet
Before loading the heated billet into the extrusion press, a release agent or lubricant is applied to both the billet and the die. This step ensures that the soft aluminum flows smoothly through the die, preventing sticking, galling, or surface imperfections.
4. Applying Ram Pressure
A hydraulic ram or press—capable of exerting up to 15,000 tons of force—slowly pushes the billet into the container and toward the die. As the billet moves forward, it expands to fill the container walls, and pressure builds until the aluminum begins to flow through the die opening. The force and speed of the ram are precisely controlled to achieve optimal extrusion quality.
5. Extrusion and Profile Formation
Under extreme pressure, the softened aluminum is forced through the die, emerging in the full cross-sectional shape of the profile. The continuous extruded length is immediately supported by a puller mechanism to guide it along the runout table and maintain dimensional stability.
6. Cooling and Quenching
As the newly formed extrusion exits the die, it is rapidly cooled—often using water sprays or air fans—along the runout table. This quenching step locks in mechanical properties and prevents unwanted grain growth or distortion. Uniform cooling is vital for achieving consistent hardness and dimensional accuracy throughout the length of the profile.
7. Shearing and Handling
Once the extrusion reaches the desired length or the end of the runout table, it is sheared or cut into manageable sections for further processing. Automated handling systems are often used to improve efficiency and minimize manual labor during this stage.
Every phase of the extrusion process is closely monitored, with temperature, pressure, and speed controls to ensure the finished product meets strict quality standards.
8. Cooling Room
After initial quenching, extruded profiles are transferred to a cooling room or area to reach ambient temperature. This additional cooling step ensures the aluminum is sufficiently stabilized before further processing or handling.
9. Stretching and Straightening
Natural twisting, bowing, or curving can occur during extrusion due to internal stresses. To correct these deformations, the profile is clamped at both ends and stretched until it meets precise straightness and dimensional tolerances specified in the design. This step is critical for applications requiring tight fit and alignment.
10. Cutting, Finishing, and Aging
Once cooled and straightened, aluminum extrusions are cut to final lengths—usually 8 to 12 feet, but sometimes longer for industrial or architectural applications. The profiles are then trimmed to remove any rough edges or excess material.
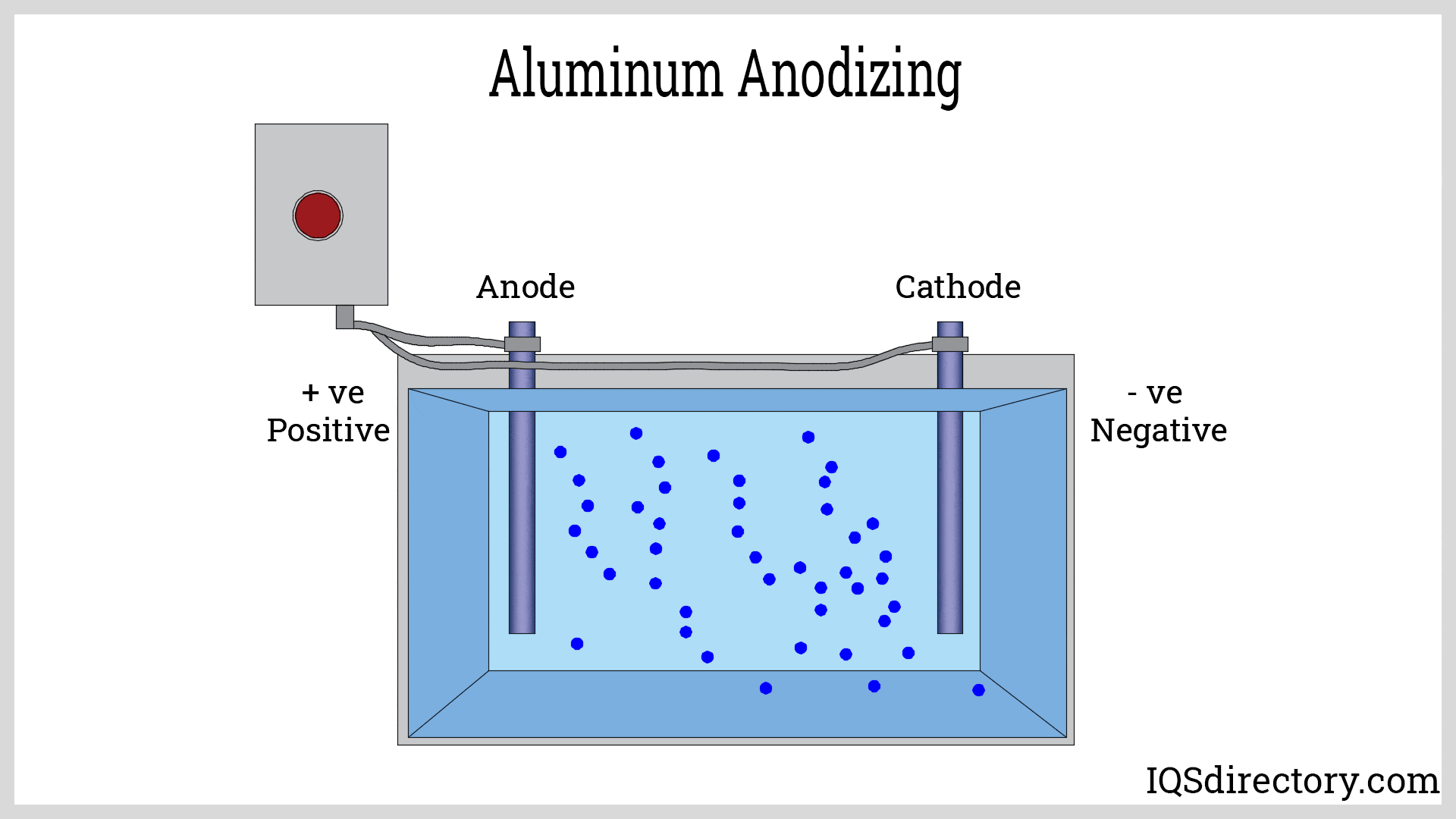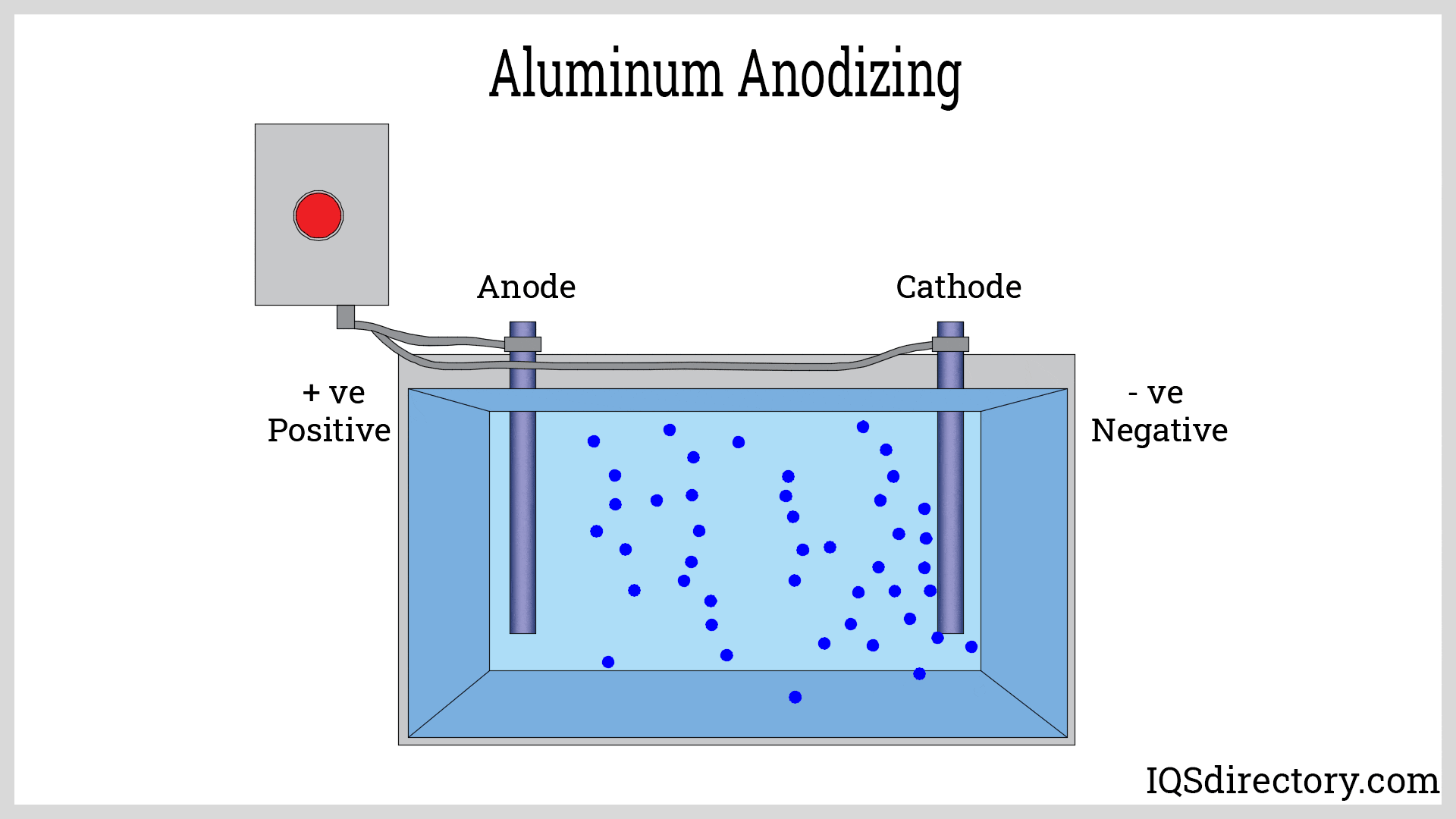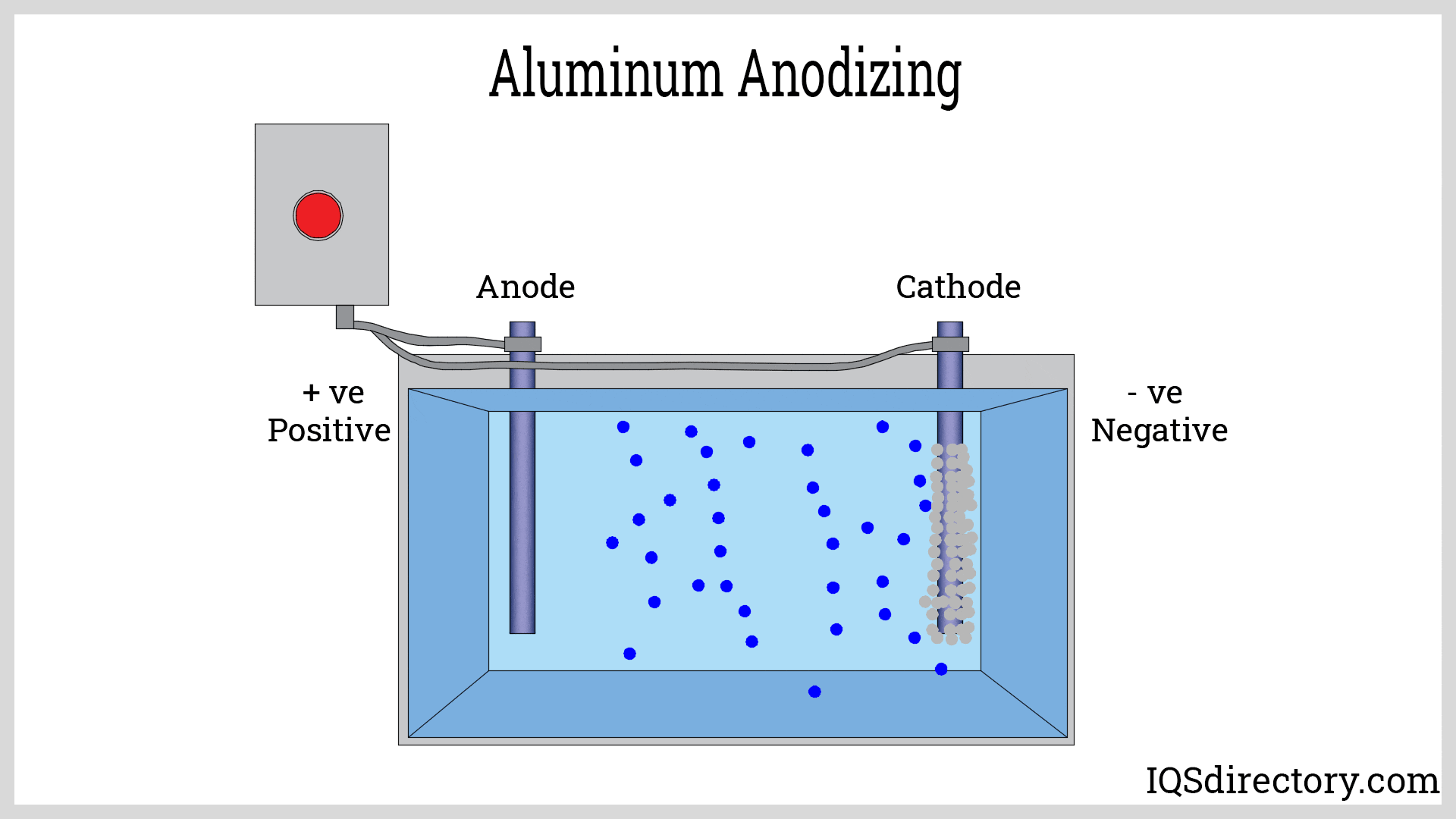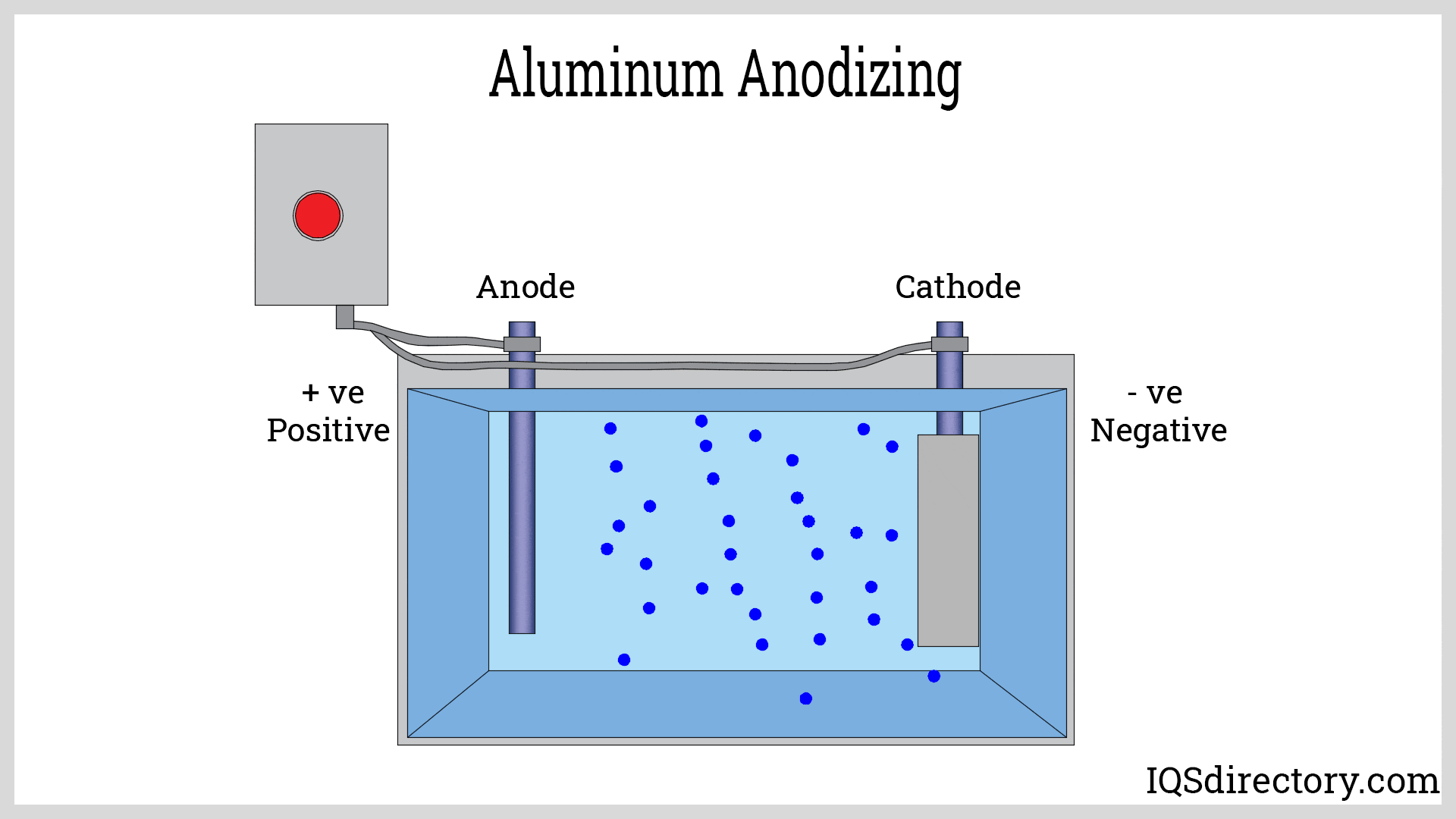
Additional tempering, known as aging, may be performed in a controlled oven to further enhance the strength, hardness, and mechanical properties of the aluminum alloy. Surface finishing options such as anodizing, powder coating, or painting can also be applied, depending on end-use requirements.

Types of Aluminum Profiles and Their Applications
The selection of an aluminum profile depends on a diverse set of factors, including application, load requirements, environment, and desired appearance. Manufacturers produce a wide range of profile types, thicknesses, alloys, and shapes to serve the specific needs of industries such as construction, transportation, electronics, and consumer goods.
Aluminum profile types include:
Hollow Profiles
Hollow aluminum profiles feature a cross-section that forms a closed cavity or multiple cavities. This design offers an excellent strength-to-weight ratio, making hollow extrusions ideal for lightweight structural applications, frames, supports, and enclosures. Common examples are aluminum tubing, rectangular and square tubes, and multi-chamber profiles for window and door frames.
Solid Profiles
Solid aluminum profiles are completely open, without any closed internal sections. These versatile extrusions are available in a variety of forms, such as bars, rods, channels, and angles, and are widely used for mechanical supports, brackets, and architectural details.
Open-End Profiles
Open-end profiles combine features of hollow and solid sections, often providing channels or slots that facilitate assembly, mounting, or cable management. T-slot extrusions are a popular example, allowing for rapid construction of modular frames, workstations, automation equipment, and machine guards in industrial settings.
Semi-Enclosed Profiles
Semi-enclosed profiles possess partially open and partially closed cavities, such as a rectangle with an open slot. These designs are frequently used in applications that require strength, rigidity, and the ability to integrate hardware or conceal wiring.
All aluminum profile shapes must conform to strict geometric tolerances and dimensional specifications, often defined by computer-aided design (CAD) models. This precision ensures compatibility with mating parts and reliable performance in demanding applications.

Understanding Profile Complexity: Categories of Difficulty
When selecting or designing an aluminum extrusion profile, it is important to consider the complexity and manufacturability of the chosen shape. These factors influence not only the cost and lead time but also the mechanical properties and suitability for specific applications. Here are the key categories used to evaluate profile difficulty:
- Shape Factor: The shape factor refers to the total area of all surfaces of the profile, influencing the extrusion pressure required and the die design's complexity.
- Complexity: Profiles are graded from A (least complex) to N (most complex) based on features such as wall thickness variations, internal cavities, and intricate geometries. Highly complex profiles may require advanced tooling and process controls.
- Material Utilization: Maximizing aluminum utilization means designing profiles that use material efficiently, reducing waste and cost per part while maintaining required strength and performance.
- Cost Considerations: The price of an aluminum profile is directly related to its complexity, required tolerances, surface finish, and alloy type. More complex profiles demand higher initial tooling investments and longer production times.
Looking to optimize your part design for aluminum extrusion?
Compare leading aluminum extrusion companies or request expert advice on the best profile geometry for your application.
Benefits of Using Aluminum Profiles
Aluminum extrusions offer a broad range of advantages that make them the material of choice for countless structural and functional applications. Key benefits include:
- Lightweight Strength: Aluminum profiles deliver high structural integrity and strength-to-weight ratio, making them ideal for aerospace, transportation, and load-bearing architectural applications.
- Corrosion Resistance: Naturally forming oxide layers give aluminum excellent resistance to corrosion, even in outdoor or marine environments. Surface treatments can further enhance durability.
- Design Flexibility: The extrusion process supports complex, intricate shapes and custom cross-sections that are difficult or impossible to achieve with other manufacturing methods.
- Thermal and Electrical Conductivity: Aluminum conducts heat and electricity efficiently, making extruded profiles suitable for heat sinks, electrical enclosures, and electronic device housings.
- Ease of Assembly: Many profiles are designed with features such as T-slots, channels, or holes, simplifying assembly and allowing for modular construction without welding or special fasteners.
- Sustainability: Aluminum is fully recyclable without loss of properties, supporting eco-friendly manufacturing practices and circular economy initiatives.
- Cost-Effectiveness: High production efficiency and minimal waste make aluminum extrusion a competitive choice for both large-scale and custom manufacturing.
Curious about real-world uses of aluminum profiles?
Explore how industries leverage aluminum extrusions for frames, supports, enclosures, and more.
Common Aluminum Profile Applications
- Construction & Architecture: Curtain walls, window and door frames, structural glazing, handrails, and decorative trims.
- Industrial Automation: Modular machine frames, conveyor systems, safety guards, robotic arms, and workstations.
- Transportation: Automotive body parts, trailer frames, marine components, and aerospace structural members.
- Electronics: Heat sinks, housings, enclosures, and cable management channels.
- Consumer Goods: Furniture, sports equipment, display systems, and retail fixtures.
- Renewable Energy: Solar panel frames, mounting systems, and wind turbine components.
Need help selecting the right aluminum profile for your project?
Browse aluminum profile options or get expert advice tailored to your specific industry and use case.
Factors to Consider When Selecting Aluminum Profiles
Choosing the best aluminum profile for your application involves careful evaluation of several decision factors, including:
- Alloy Selection: Different aluminum alloys offer unique combinations of strength, ductility, corrosion resistance, and machinability. Common alloys include 6061, 6063, and 6082.
- Profile Geometry: Consider the cross-sectional shape, wall thickness, and required features to ensure compatibility with your design and assembly process.
- Surface Finish: Options such as anodizing, powder coating, and painting can enhance appearance, durability, and corrosion resistance.
- Mechanical Properties: Evaluate load-bearing requirements, bending strength, and fatigue resistance for your intended use.
- Length and Tolerance: Specify the required profile length and dimensional tolerances to meet your assembly and quality standards.
- Quantity and Lead Time: Discuss production volumes and delivery timelines with your aluminum profile supplier to ensure timely project completion.
Ready to start your aluminum extrusion project?
Request a quote or find a trusted aluminum profile manufacturer in your area.
Choosing the Right Aluminum Profiles Manufacturer
Achieving the best results with aluminum profiles depends on partnering with a reputable, experienced manufacturer who understands your application requirements and can deliver consistent product quality. Here’s how to ensure you make the right choice:
- Compare Multiple Suppliers: Evaluate at least four or five aluminum profile manufacturers using our comprehensive directory. Assess their capabilities, experience, and product range.
- Review Business Profiles: Each supplier’s business profile page highlights their expertise, certifications, and available services. Look for case studies and project portfolios relevant to your industry.
- Request Quotes and Samples: Use our simple RFQ form to contact several companies with your requirements. Compare lead times, pricing, and custom manufacturing options.
- Preview Company Websites: Use our proprietary website previewer to research each manufacturer’s specializations, customer reviews, and technical resources.
- Direct Communication: Reach out via contact forms to discuss your project in detail, request design input, or arrange for technical consultation.
What should you ask your aluminum profiles supplier?
- Which alloys and finishes do you offer for custom profiles?
- Can you provide CAD design assistance or prototyping services?
- What are your minimum order quantities and typical lead times?
- Are you certified for quality management (e.g., ISO 9001)?
- How do you ensure dimensional and surface quality for each batch?
Make your aluminum profile sourcing process simple and transparent—
Compare trusted aluminum profile suppliers now or request a quote for your next project.
Frequently Asked Questions About Aluminum Profiles
How do I determine which aluminum profile is best for my application?
Start by evaluating your strength, weight, and assembly requirements. Then, consult with an experienced extrusion engineer or supplier to select the optimal geometry and alloy for your use case.
What are the lead times for custom aluminum profile manufacturing?
Lead times vary by project complexity, order volume, and finishing requirements, but most suppliers offer timelines from a few weeks for standard profiles to several months for fully custom extrusions. Early communication with your supplier is key to meeting project deadlines.
Are aluminum profiles environmentally friendly?
Yes. Aluminum is 100% recyclable, and many manufacturers utilize recycled content in their billets. Energy-efficient production and closed-loop recycling make aluminum extrusions a sustainable choice for modern construction and manufacturing.
Can aluminum profiles be machined, welded, or assembled with other materials?
Absolutely. Aluminum extrusions can be cut, drilled, machined, welded, and easily joined with standard fasteners, enabling seamless integration into multi-material assemblies.
Where can I find design guides or technical resources for aluminum profiles?
Visit our design resources for engineering data, CAD files, and best practices for aluminum profile selection and application.
Get Started With Aluminum Profiles
Aluminum profiles are foundational building blocks for modern industry, combining strength, versatility, and sustainability in a single solution. Whether you need standard shapes or custom extrusions, our network of leading aluminum extrusion companies can help you achieve your project goals—from design consultation and prototyping to high-volume production and finishing.
Ready to take the next step?
Request a fast, free quote or explore our selection of aluminum profiles to find the perfect match for your application.





 Alloy Suppliers
Alloy Suppliers Aluminum
Aluminum Aluminum Extrusions
Aluminum Extrusions Copper-Brass-Bronze
Copper-Brass-Bronze Nickel
Nickel Magnets
Magnets Stainless Steel
Stainless Steel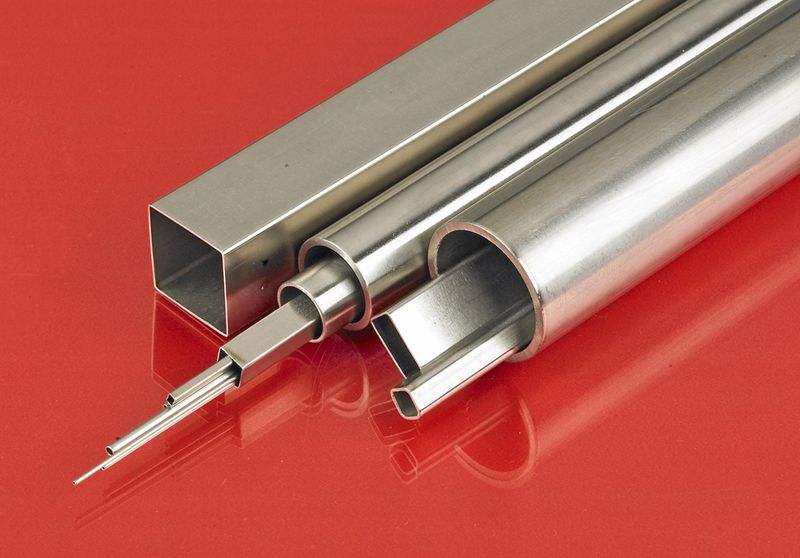 Stainless Steel Tubing
Stainless Steel Tubing Steel Service Centers
Steel Service Centers Titanium
Titanium Tungsten
Tungsten Wire Rope
Wire Rope Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services